What Causes St Segment Depression

The st segment represents the interval between ventricular depolarization and repolarization.
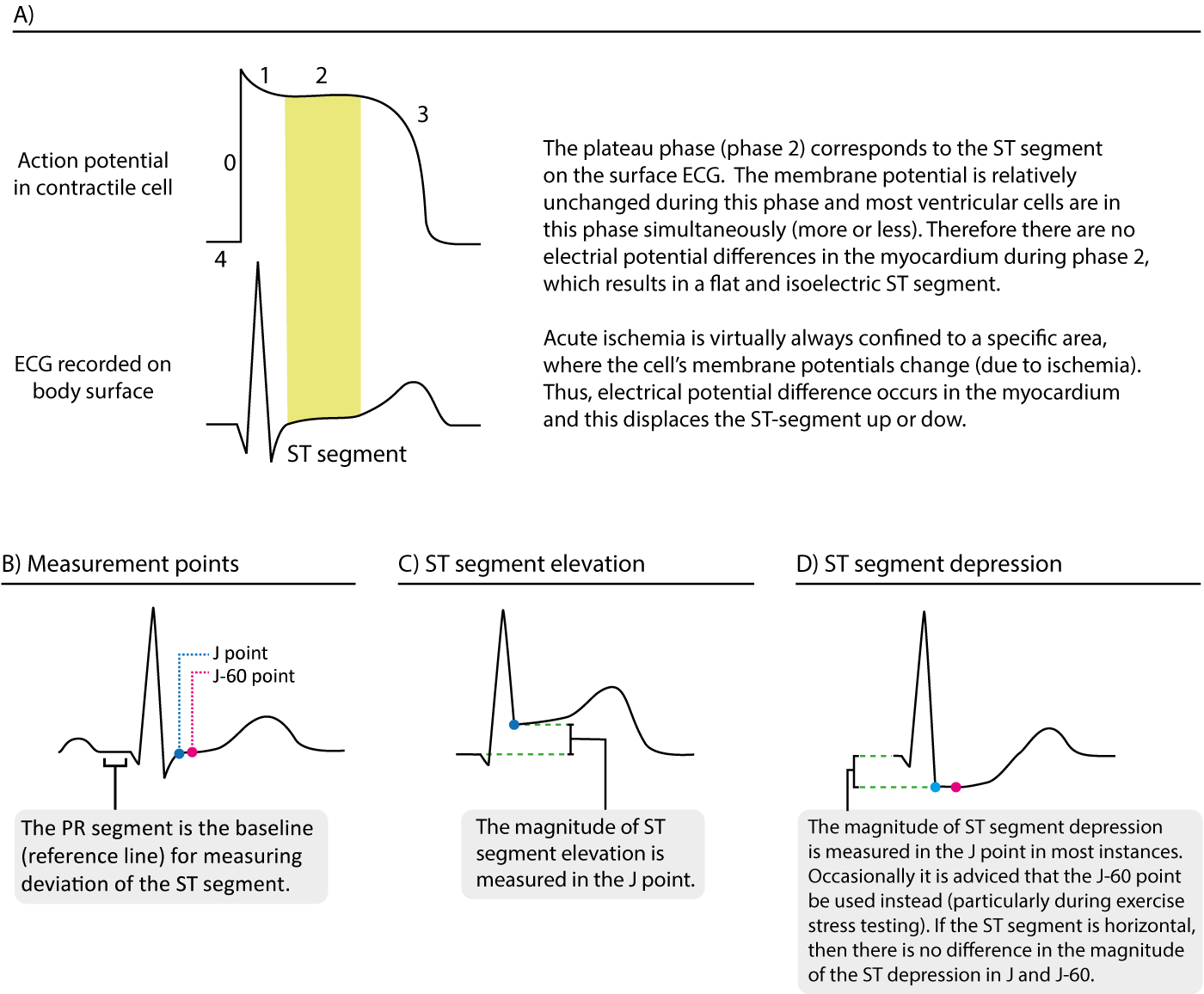
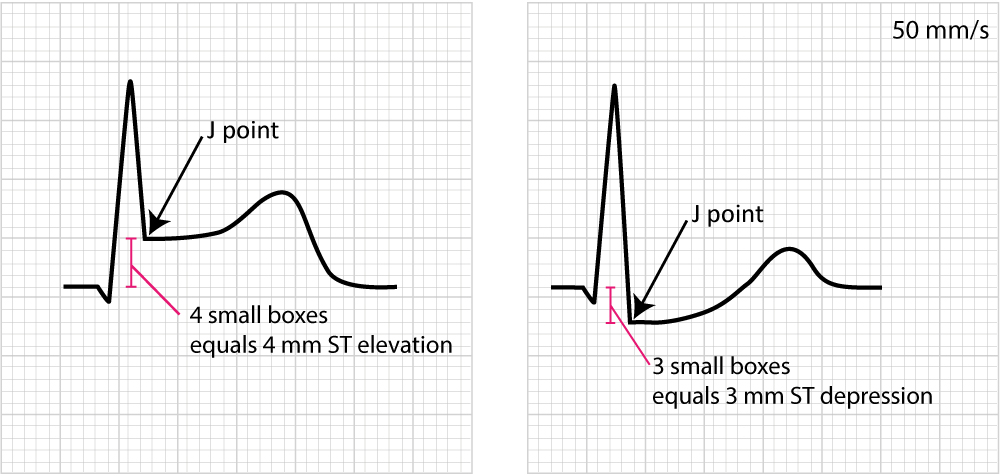
What causes st segment depression. The st segment can become elevated or depressed. Subendocardial ischemia or even infarction. The st segment is the flat isoelectric section of the ecg between the end of the s wave the j point and the beginning of the t wave. St segment depression can occur during adenosine myocardial perfusion imaging and is an independent predictor of subsequent cardiac events and worse outcome particularly in association with ischemic defects.
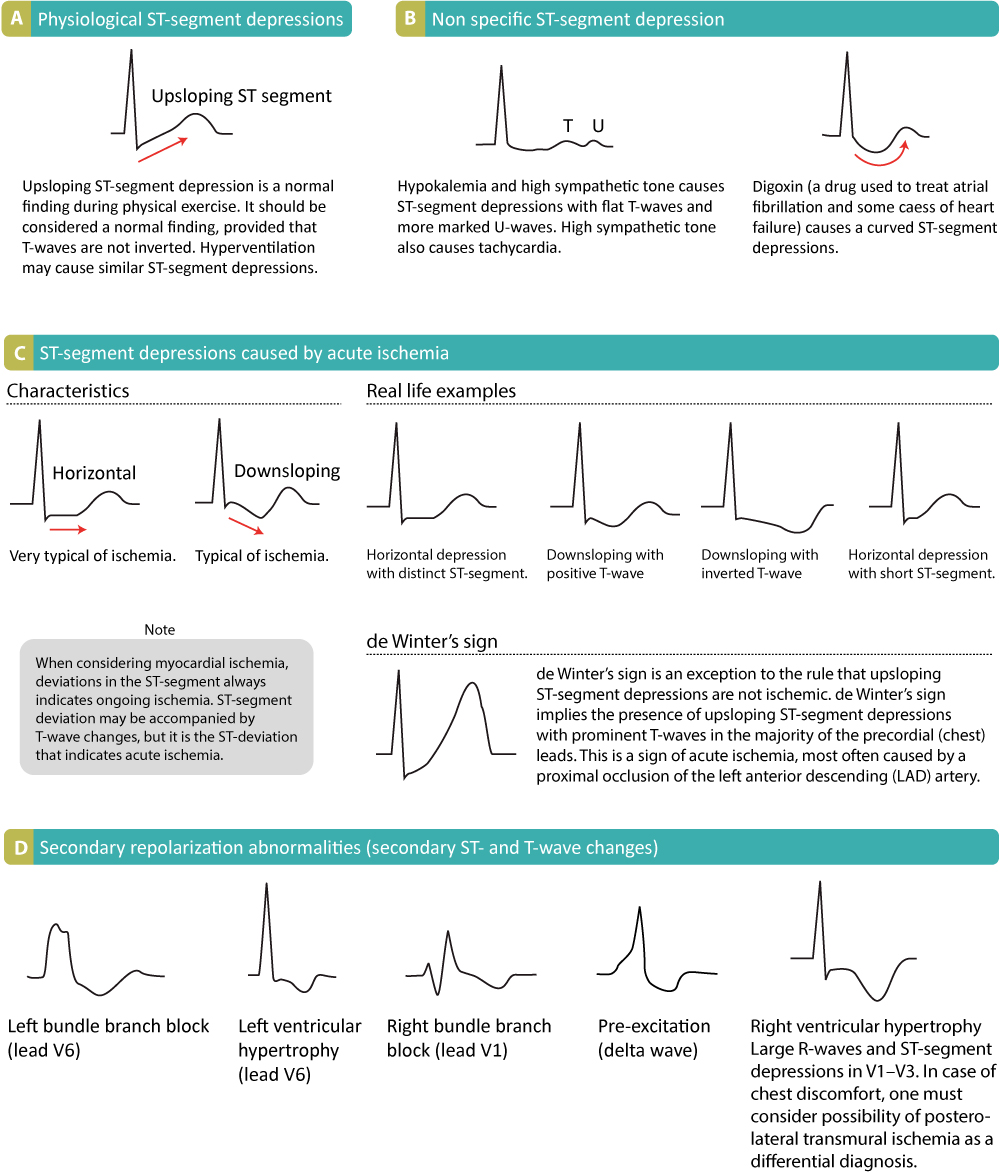
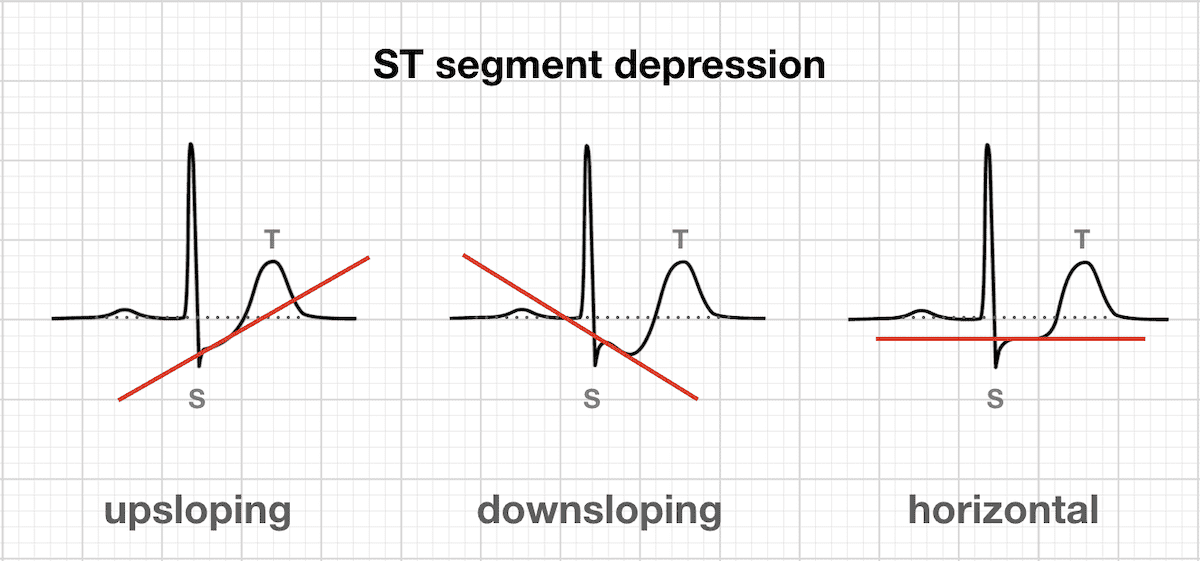
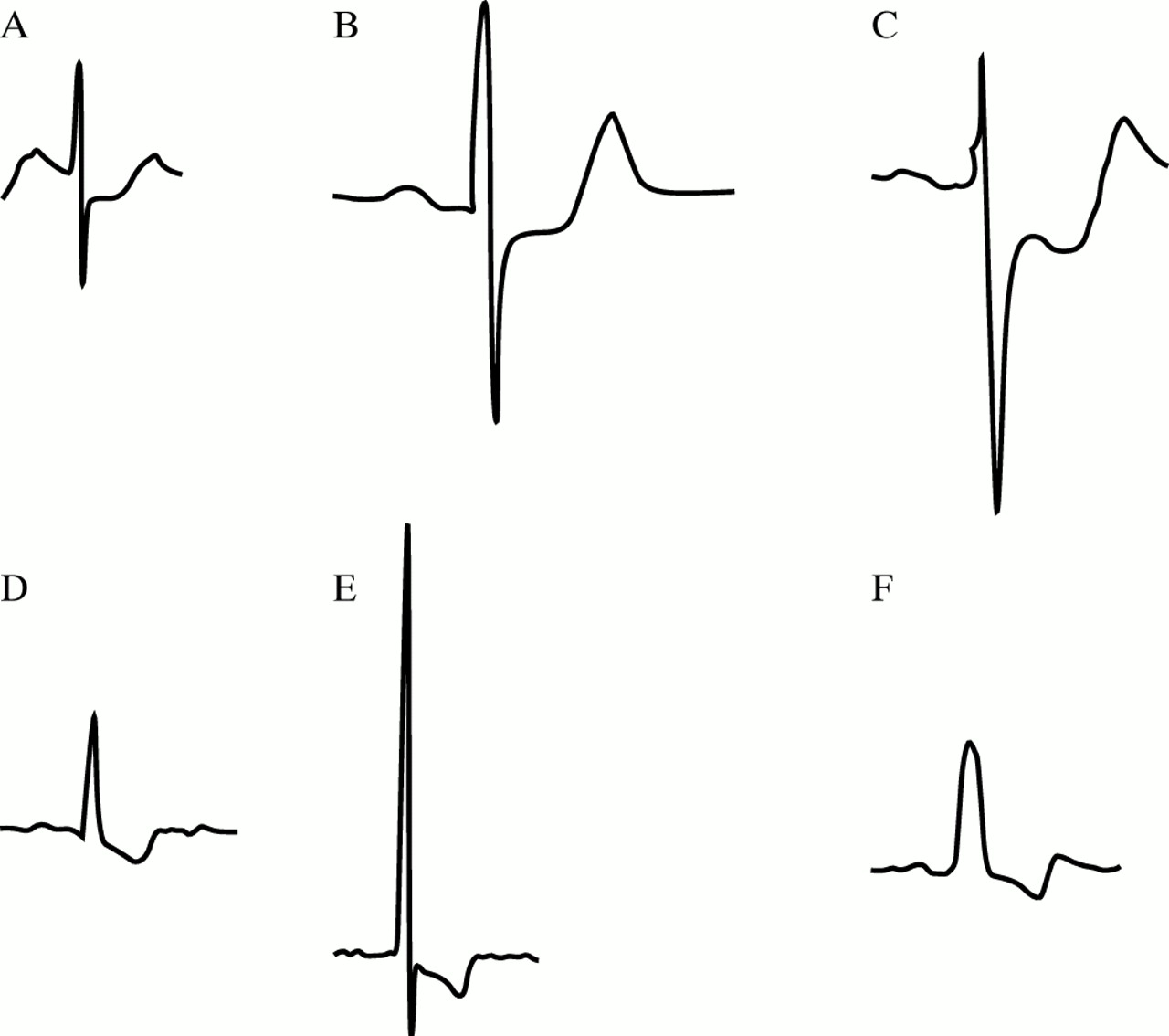
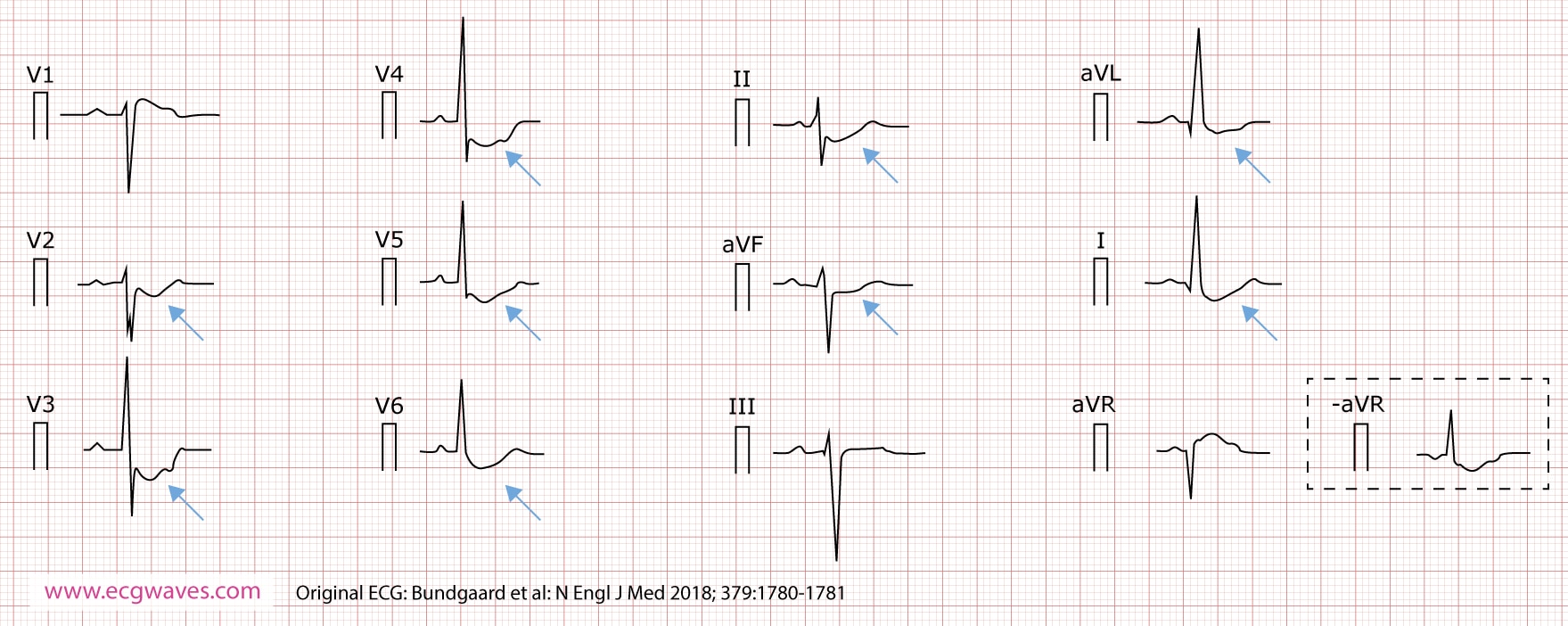
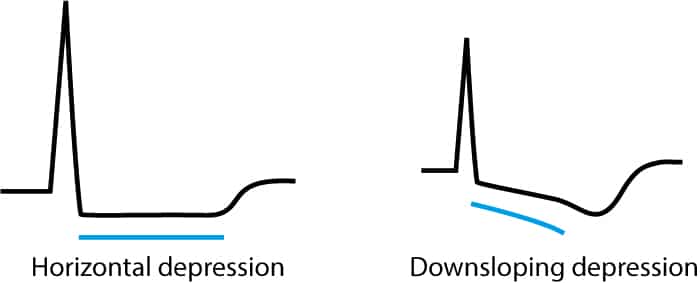
St segment depression due to acute myocardial ischemia. Depression of the st segment and inversion of the t wave are common electrocardio graphic abnormalities. St segment depressions caused by ischemia are characterized by a horizontal or downsloping st segment. Otherwise ischemia is unlikely to be the cause of the st segment depression.
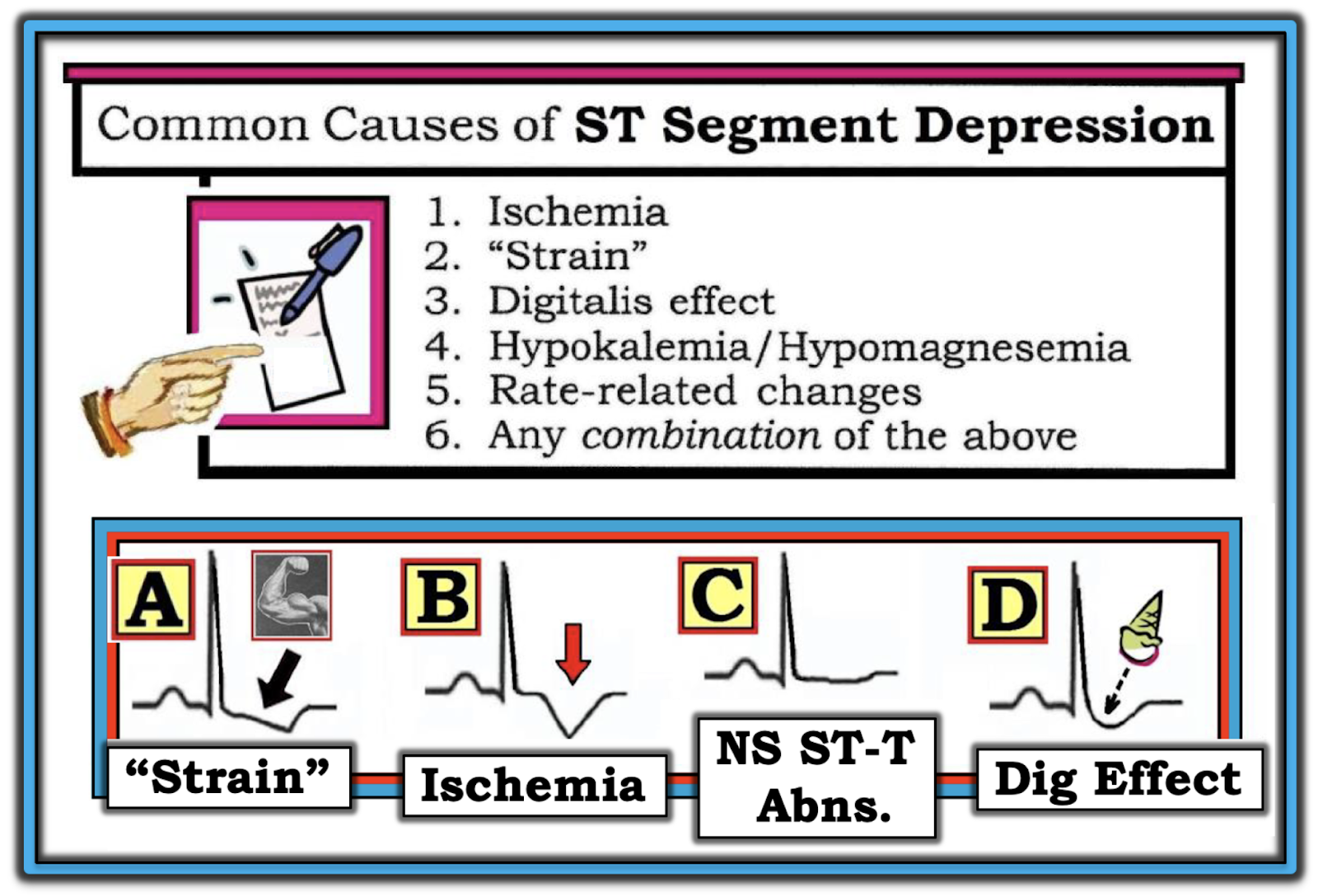
The most important cause of st segment abnormality elevation or depression is myocardial ischaemia or infarction. Myocardial ischemia nstemi. Causes of st segment depression include myocardial ischemia digoxin effect ventricular hypertrophy acute posterior myocardial infarction pulmonary embolus left bundle branch block. Secondary st segment depressions occur in the following conditions.
Indeed north american and european guidelines assert that the st segment must be either downsloping or horizontal. Differential diagnosis of st segment depression normal variants or artifacts. Left ventricular hypertrophy right ventricular hypertrophy left bundle branch block right bundle branch block pre excitation pacemaker stimulation in the right ventricle. Subendocardial means non full thickness ischemia.
In contrast st elevation. Hypokalemia st segment depression t wave flattening hyperkalemia multiple possible changes. Reciprocal change in stemi. T wave inversion in the anterior precordial leads may be seen in cases of acute pulmonary embolism while flat tened t waves with prominent u waves and st segment depression may reflect hypokalemia or digitalis therapy.
Non q wave myocardial infarction reciprocal changes in acute q wave myocardial infarction e g st depression in. Pseudo st depression wandering baseline due to poor skin electrode contact physiologic j junctional depression with sinus tachycardia most likely due to atrial repolarization. Results in prolonged qt hypermagnesemia increased t wave amplitude hypercalcemia short t wave with shortened qt.