Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma Histology
Histopathology falls within the larger field of pathology.
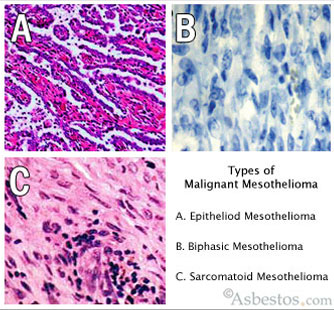
Sarcomatoid mesothelioma histology. I pleural mesothelioma is a cancer that develops in tissue surrounding the lungs ii pericardium mesothelioma originates in the pericardium membrane lining the heart iii peritoneal mesothelioma starts growing around the abdominal organs and iv tunica vaginalis mesothelioma is a cancer that forms on the membrane lining the testicles. Sarcomatoid mesothelioma is the least common cell mutation caused by asbestos exposure. Histopathology is the study of diseased cells. Sarcomatoid mesothelioma is a rare cell type caused by asbestos exposure.
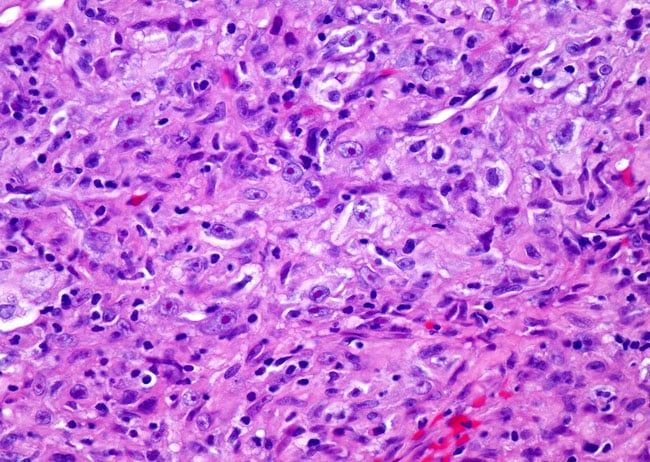
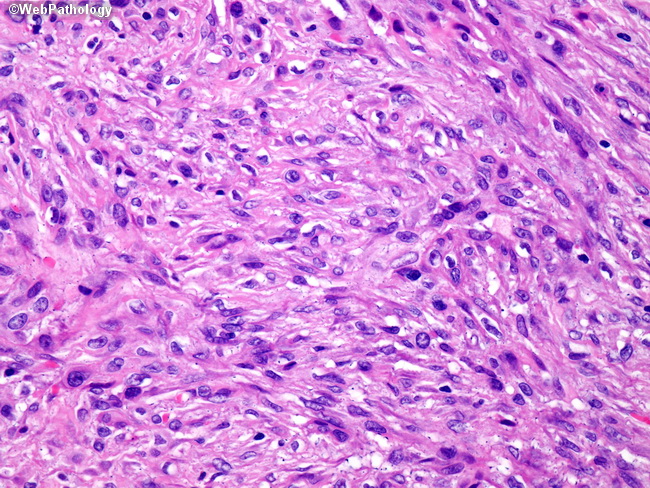
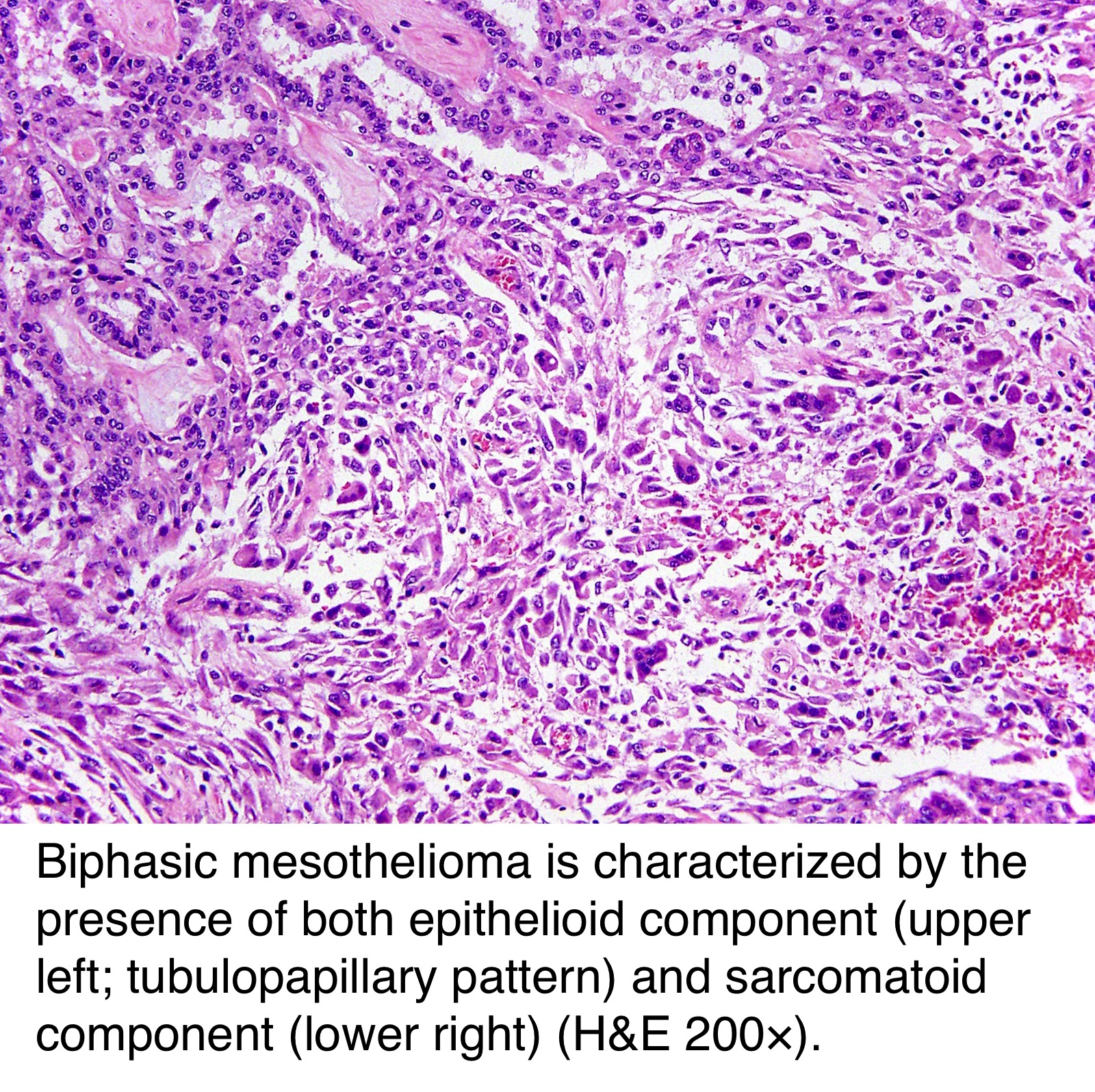
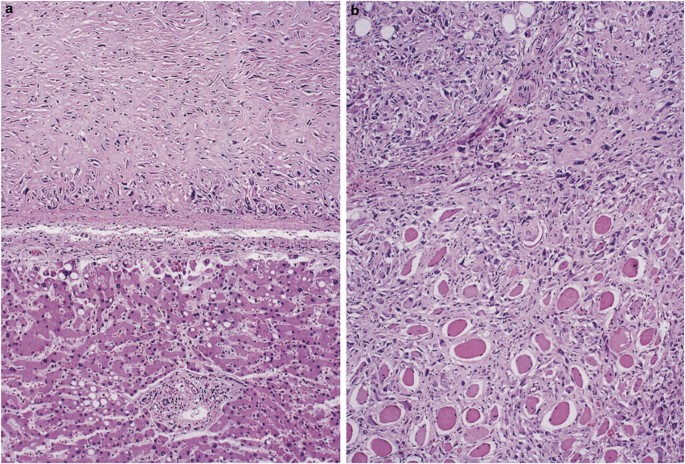
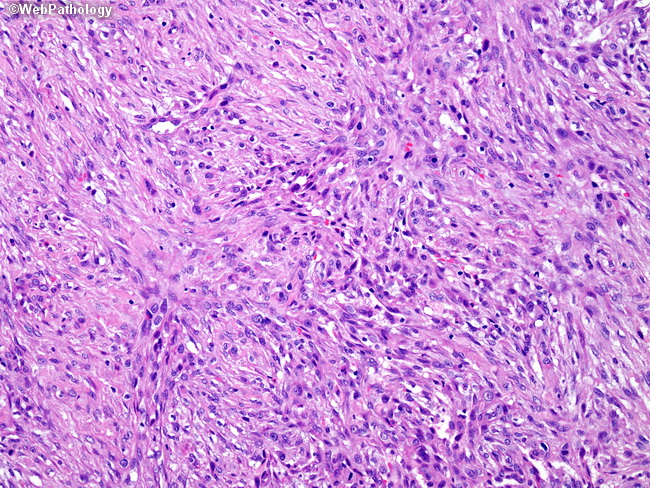
Sarcomatoid mesothelioma is a more treatment resistant type of mesothelioma. It can occur in the linings of the lungs abdomen and heart. Pathologists recognize sarcomatous mesothelioma cells by their long spindle like shape. Mesothelioma can be categorized histologically as epithelioid type sarcomatoid type biphasic type desmoplastic type among others.
Mesothelioma is classified into four main types based on the part of the body. Sarcomatoid mesothelioma is the least common cell type of mesothelioma and known for its abnormal spindle shape. Sarcomatoid mesothelioma is the rarest of the mesothelioma cell types accounting for between 10 and 20 of all mesothelioma cases. Mesothelioma histology involves the study of cancerous mesothelial cells.
It can take many forms. Histology is a branch of biology that involves the study of cells and tissues. However immunohistochemical analyses of sarcomatoid mesothelioma the less common type are limited and its distinction from other tumors of the chest wall lung and pleura is often problematic. Understanding sarcomatoid cell type.
Sometimes referred to as spindle cell mesothelioma sarcomatoid cells are recognized by their oval spindle shape. Defining characteristics of sarcomatoid mesothelioma cells when determining what type of mesothelioma a patient has physicians will use histology the study of cells to analyze tumor cells and differentiate type. Sarcomatous cells spread quickly and make up about 10 to 20 of all mesothelioma cases. Sarcomatoid cells are sometimes hard to recognize as they can appear very similar to normal healthy cells.
Consequently there are many diseases to be differentiated when the diagnosis of mesothelioma is based on histological analyses. The immunohistochemical characteristics of epithelioid malignant mesothelioma are well described. Chemotherapy and radiation are the most common treatment options.