Diabetes Insipidus Treatment Guidelines
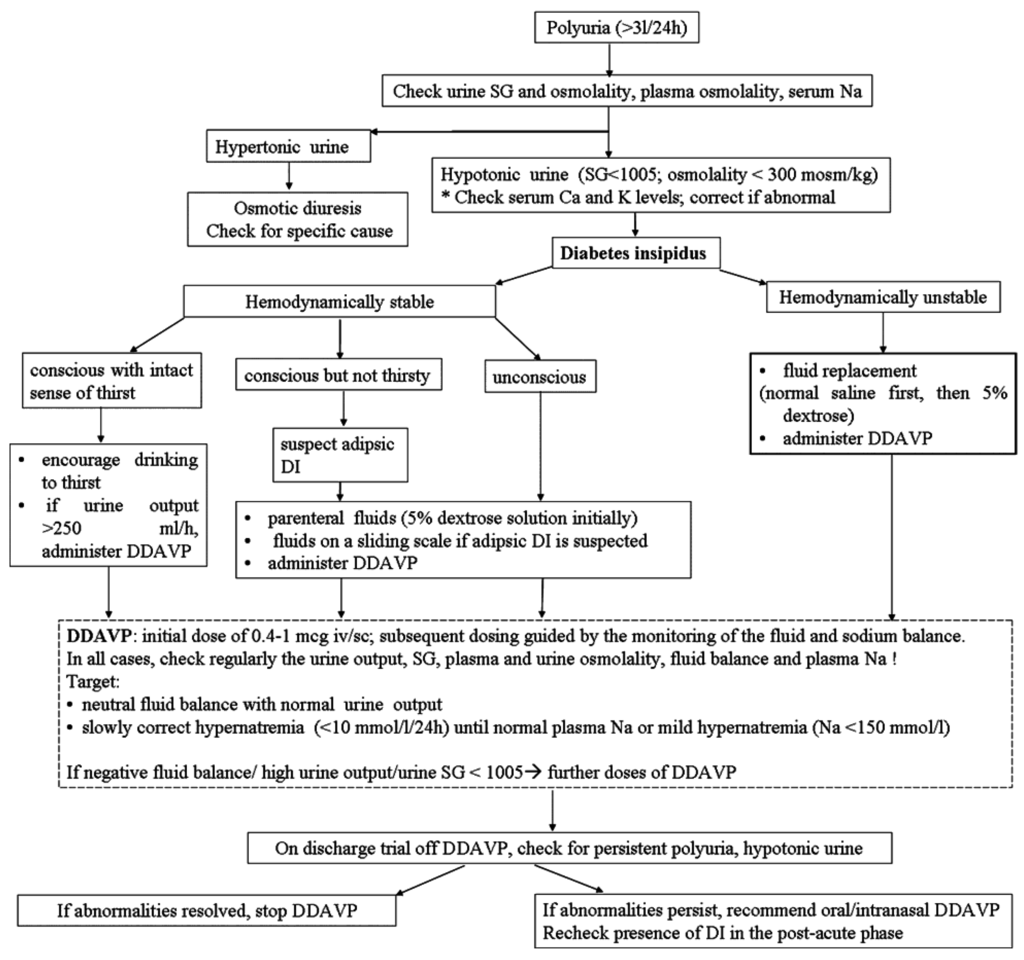
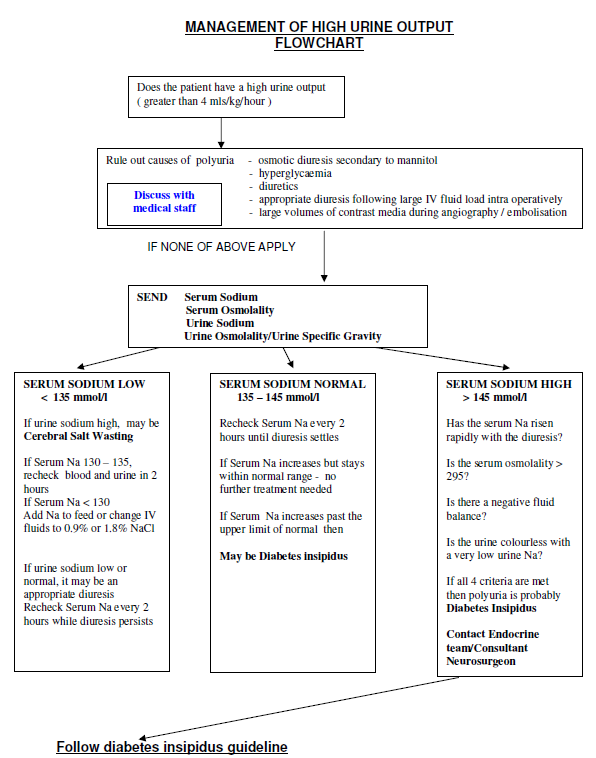
It also includes an algorithm for the management of a high urine output and a four hourly fluid balance chart.
Diabetes insipidus treatment guidelines. Consideration should be given to. Disorder characterized by polydipsia polyuria and formation of inappropriately hypotonic dilute urine. If you have diabetes insipidus. Specific treatment for diabetes insipidus will be determined by your physician based on.
Repeat the dose when urine output is between 200 and 250 ml h for 2 h with osmolality 200 mosm kg or urinary specific gravity 1005. Diabetes insipidus is present when the serum osmolality is raised 295milliosmol kg with inappropriately dilute urine urine osmolality 700milliosmol kg. Mild cranial diabetes insipidus may not require any medical treatment. The 2020 standards of medical care in diabetes includes all of ada s current clinical practice recommendations and is intended to provide clinicians patients researchers payers and others with the components of diabetes care general treatment goals and tools to evaluate the quality of care.
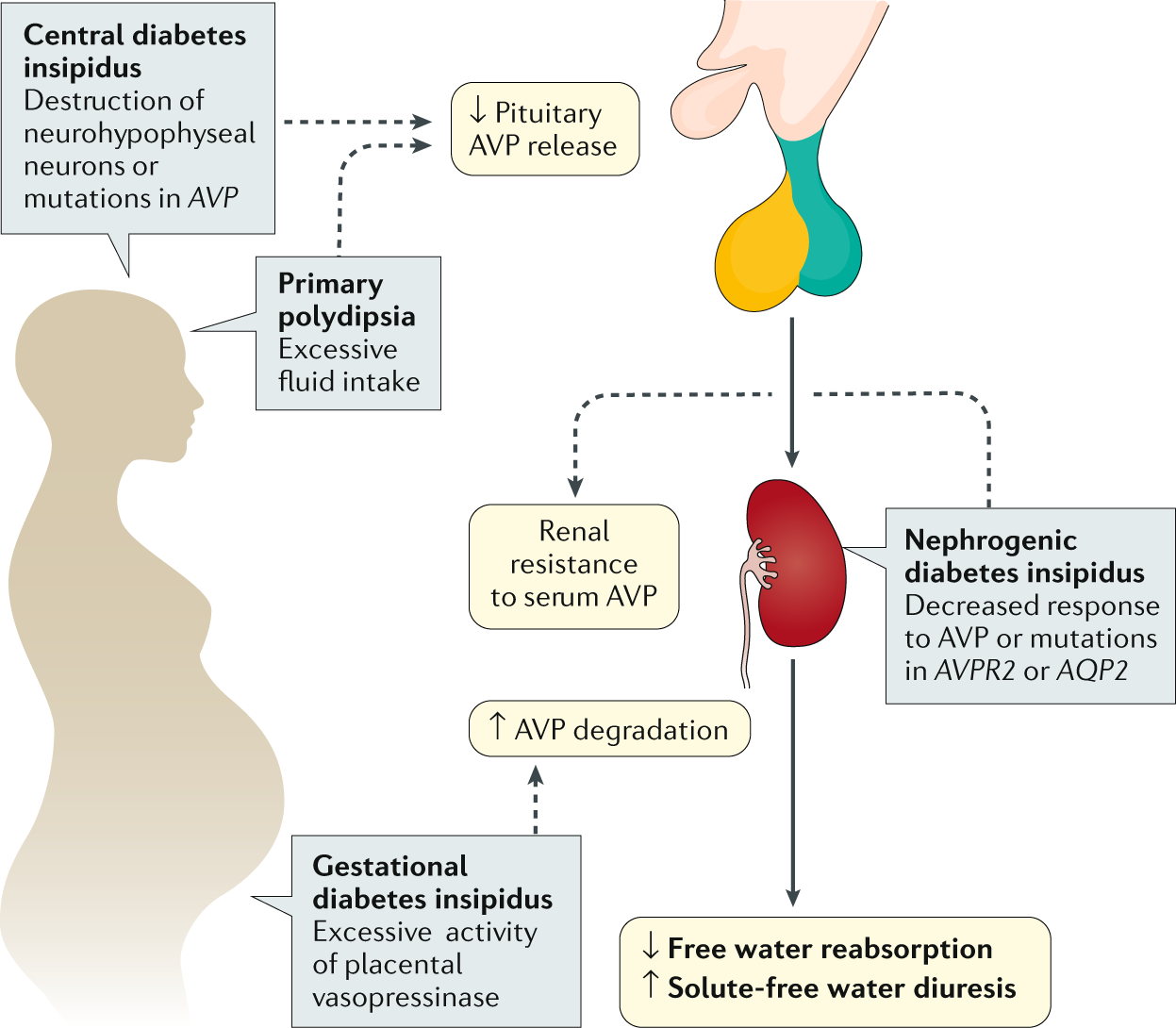
Also called arginine vasopressin or avp. If this is the case you may be able to ease your symptoms by increasing the amount of water you drink to avoid dehydration. As long as you take your medication and have access to water when the medication s effects wear. When oral intake is inadequate and hypernatremia is present replace losses with dextrose and water.
This guideline has been written to aid in the diagnosis post operative management monitoring and potential complications of diabetes insipidus. Central diabetes insipidus di due to reduced synthesis or release of arginine vasopressin avp from the hypothalamo pituitary axis. The major symptoms of central diabetes insipidus di are polyuria nocturia and polydipsia due to the concentrating defect. Replacement of previous and ongoing fluid losses is also important.
Treatment of this disorder is primarily aimed at decreasing the urine output usually by increasing the activity of antidiuretic hormone adh. Baseline investigations should include urea and electrolytes full ward test of urine and paired serum and urine osmolality. Most patients with diabetes insipidus di can drink enough fluid to replace their urine losses. Cranial diabetes insipidus is considered mild if you produce approximately 3 to 4 litres of urine over 24 hours.
If you have a medical emergency a health. The recommendations are based on an extensive review of the clinical diabetes literature. Maintenance of water balance. And nephrogenic di due to renal inse.
Patient unable to maintain oral fluid intake urine output higher than fluid intake hypernatremia.