Creatine Phosphate Atp Yield

Produce 4 atp net yield is 2 atp.
Creatine phosphate atp yield. Creatine phosphate cp like atp is stored in muscle cells. This process yields 36 atp. Nad nicotinamide adenine di nucleotide. The energy released is coupled to the energy requirement necessary for the resynthesis of atp.
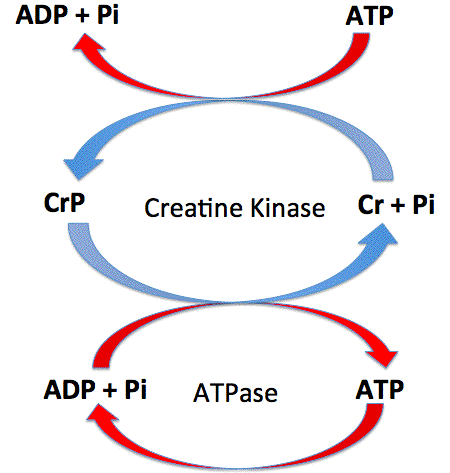
Other studies have up to ten seconds. The atp cp system involves an interaction between two molecules atp and creatine phosphate or cp within the cell. Phosphocreatine reacts with adp to yield atp and creatine. The breaking of the pc bond releases 43 3 kj 10 3 kcal per mole which is considerably more than that seen in the breakdown of the high energy bonds in atp indicating that there is more than enough.
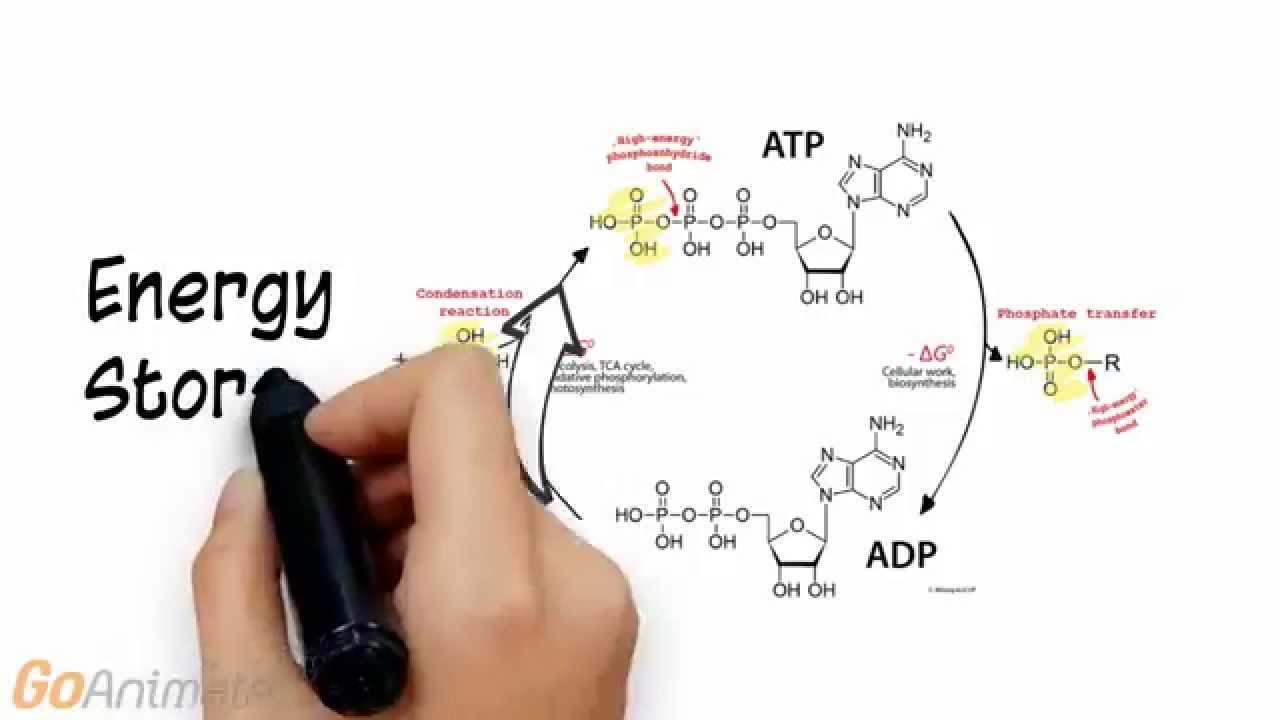
When atp s outermost phosphate bond is broken off adenosine diphosphate or adp is formed along with a great deal of energy. Donate 2 atp phase 2. Crp adp atp cr nb. This process is an important component of all vertebrates bioenergetic systems.
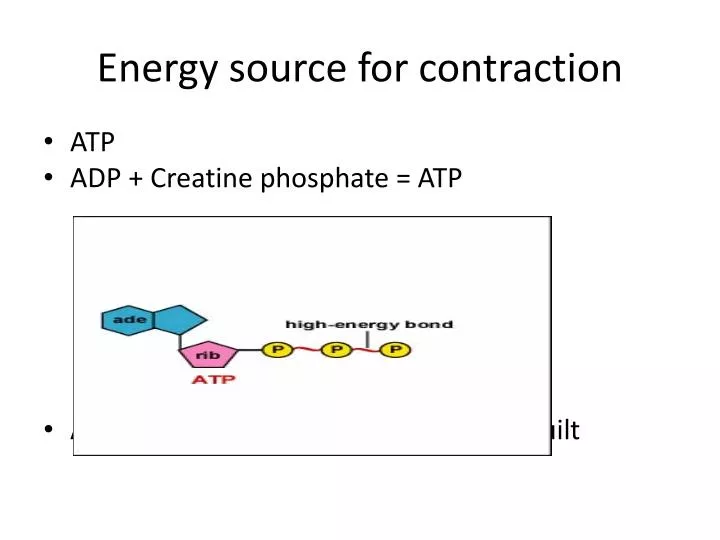
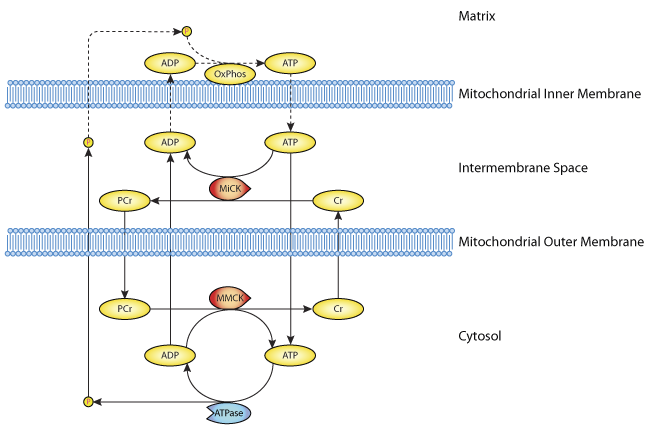
The phosphorylated creatine transfers its phosphate to adp to form atp leaving unphosphorylated creatine. Atp yield by glycolysis phase 1. Creatine phosphate comes to the rescue. Chemical reaction for creatine phosphate to atp.
The reversible reaction is catalyzed by creatine kinase. Because of this all muscle cells contain and utilize creatine phosphate which is broken down to make more atp quickly. Sprints or 3 rep squats creatine phosphate can be resynthesised however we require oxygen. This creatine can then be reconverted into creatine phosphate via the addition of a phosphate from atp catalysed by the second isoform of creatine kinase in the mitochondria during aerobic recovery.
When we rest between high intensity efforts e g. It is catalysed by the enzyme creatine kinase. The total muscular stores of both atp and cp are small. The muscles limited atp supply is used very quickly in muscle activity so the need to regenerate atp is essential.
Thus this reaction which permits the rephosphorylation of adp to atp is the immediate source of energy in muscle contraction. When it is broken down a large amount of energy is released. The cp molecule also releases a large amount of energy when the bond between its creatine and. Since the body has only about three ounces of atp at any one time however it runs out of its supply rapidly.
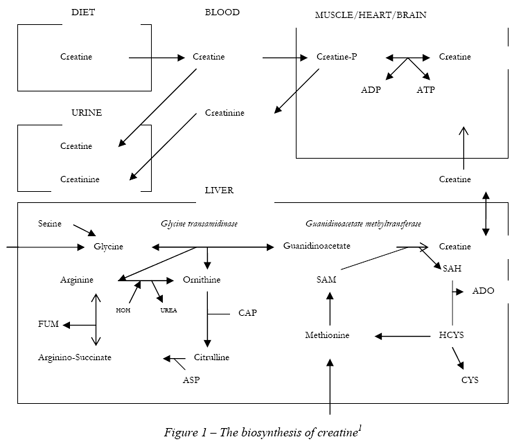
Phosphocreatine is the chief store of high energy phosphates in muscle. In the process of regeneration of atp creatine phosphate transfers a high energy phosphate to adp. When the muscle cells have the energy of atp they can act in the time it takes for alternate energy sources to be activated. Once inside the cells it is transformed into phosphocreatine by the enzyme complex creatine kinase which makes it able to donate its phosphate group to convert adenosine diphosphate adp into adenosine triphosphate atp.
Thus the amount of energy obtainable through this system is limited. One of the ways that this atp supply is regenerated is through the molecule creatine phosphate or phosphocreatine.